
Laurent expansions provide the basis for the Fourier series representation of analytical functions. Because trigonometric functions are separating the Descriptor, which appears in many physics equations, the Fourier series and its generalizations are essential in the field of physics. The spherical harmonics replace the trigonometry foundation in the Fourier series for variables of 2 factors that are regular in both dimensions.
The Fourier transform is used instead of the Fourier series for non-periodic functions. A so-called Fourier-Bessel series is obtained by exploiting orthogonality of the roots of a Bessel function of the first order. A generalized Fourier series equivalent to the Fourier series exists for any set of functions that form a full orthogonal system. This technique can even produce analytic answers in some exceptional circumstances where the Fourier series can be summed in closed form.

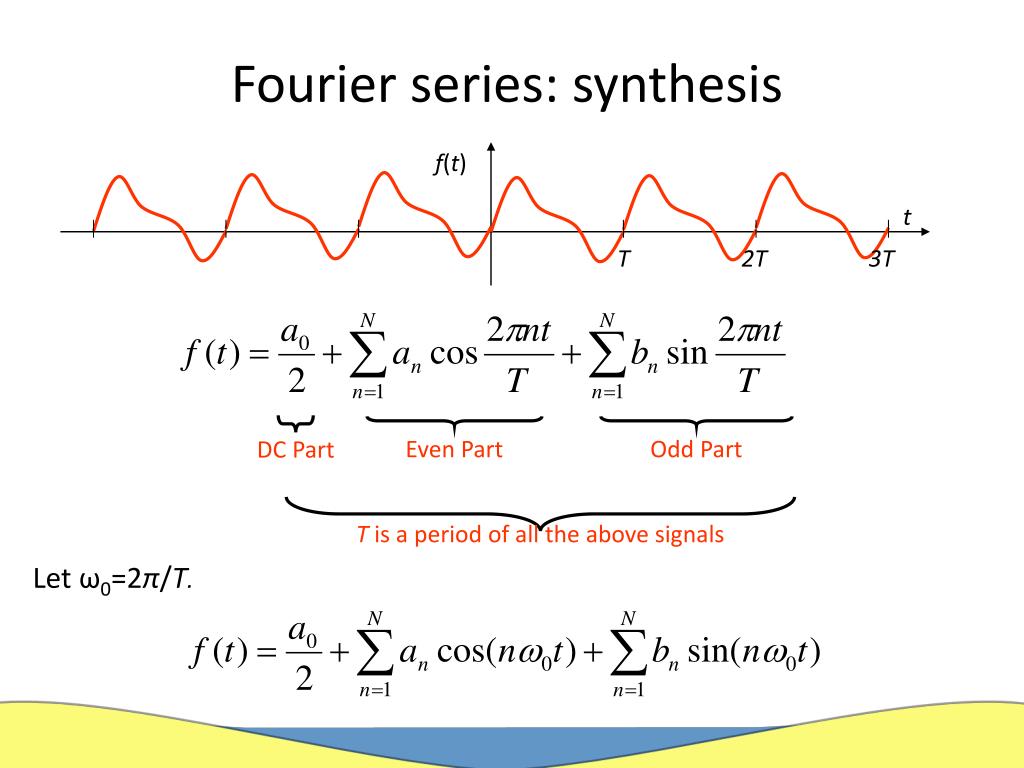
Let’s discuss fourier series formula in detail along with some important questions.īecause the principle of superposition retains for options of a linear relatively homogenous partial differential equation in the consists of a sole sinusoid, the answer for any auxiliary variable can be found by conveying the primary purpose as a Fourier series and afterward trying to plug in the quick fix for every sinusoidal component. Harmonic analysis is the study and measurement of the Fourier series, and it is extremely useful for breaking down an arbitrary periodic function into a set of simple terms that can be plugged in, solved separately, and then recombined to obtain the optimal solution to the real issue or a prediction to whatever suitability is intended to achieve or practical.
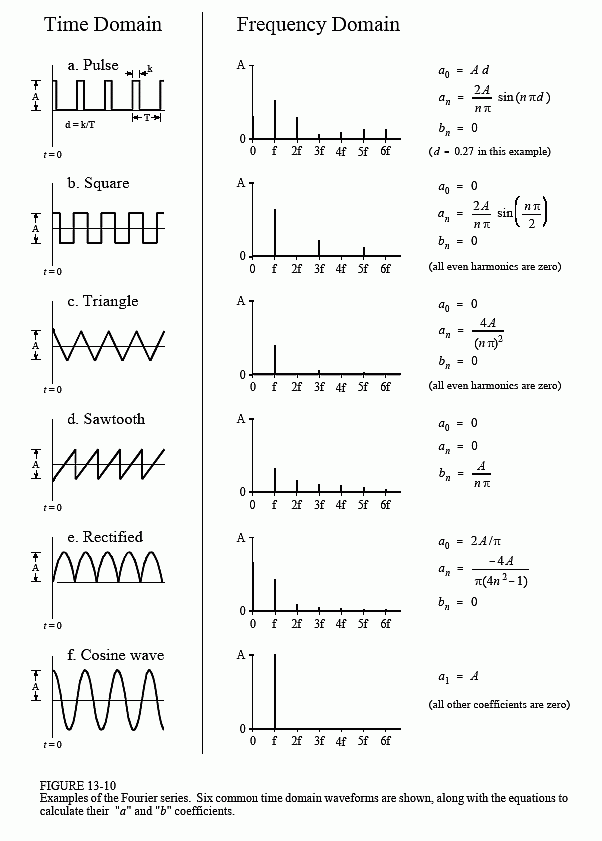
Any periodic function or periodic signal can be decomposed into the sum of a collection of simple oscillating functions, such as sines and cosines. A periodic function f(x) is expanded in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines using the Fourier series formula. Using a technique known as Fourier analysis, we can break down these periodic functions into their constituent parts. An alternating current circuit, for example, has current and voltage. Many of the phenomena investigated in the fields of engineering and science have a regular pattern.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
